Gigahertz-Optik´s ISO 17025 accredited test and calibration laboratory
Content:
Introduction
Gigahertz-Optik's in-house testing and calibration laboratory is accredited according to ISO 17025. This is proof of the high level of quality that we apply to our daily tasks. At the same time, our products benefit from this accreditation because knowledge and quality standards are already incorporated during development and throughout our production and QA processes.
External bodies regularly monitor our testing and calibration procedures. In Germany, the DAkkS (German Accreditation Body) is entrusted with this. In the USA, NVLAB (National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program) would be the corresponding authority. This independent verification saves our customers from having to conduct their own audits and in turn leads to acceptance by their customers. Due to the high requirements for an accredited test or calibration, the customer also receives the lowest possible measurement uncertainty. Furthermore, test and calibration certificates with the ILAC logo (International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation) are internationally recognized and additionally meet the requirements of some common standards, such as IATF 16949.
Since 1993, Gigahertz-Optik has had an accredited calibration laboratory for the measurands "spectral irradiance" and "spectral sensitivity".
In 2019, the accreditation was extended to include the testing laboratory with a wide range of measurands. (See 3. ISO 17025 test laboratory)
In 2022, the accreditation of the calibration laboratory was again extended for the measurands "irradiance of broadband radiometers" and "dc current".
Click here for the services of our testing and calibration laboratory.
ISO 17025 calibration laboratory
Our calibration laboratory is accredited by the DAkkS (Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle). DAkkS calibration is the highest German industrial standard. In a DAkkS calibration, a measurand is passed on. The calibration object (source or detector) serves as an artifact for the transfer of the measurand. A DAkkS-calibrated artifact can be used as a reference for further ISO 17025 accredited calibrations or tests as long as the laboratory has the appropriate accreditation.

Spectral irradiance
Spectral irradiance is the fundamental quantity in radiometry from which various measured quantities can be derived, such as:
- Integral Irradiance
- Photobiological actinic irradiance
- Photosynthetically active radiation
- Illuminance
- Colorimetry
- Radiant flux, radiant intensity, radiance, luminous flux, luminous intensity and luminance with known geometric ratios
It is defined as the power per wavelength incident on a defined surface element . You can find more information on the basics of light measurement technology on our information portal: Gigahertz-Optik GmbH Information Portal
Different source types are offered for the dissemination of the measurands:
For the wavelength range from to ,
For the wavelength range from to ,
Spectral responsivity
Spectral responsivity s( Φ is the essential parameter for the characterisation of radiometers, as well as in the measurement of monochromatic light sources, such as narrowband LEDs or lasers.
It is defined as the system response of a detector at a certain power per wavelength . The Gigahertz Optik calibration laboratory is accredited for the wavelength range from to .
Depending on the application, different types of detectors are offered for the dissemination of the measured variable:
Silicon diodes are typically used for convergent, or parallel, radiation sources with small spot diameters. Diodes of this type are also sold under the name MD-37 or PD series (PD-45 series, PD-MSD series).
For diffuse radiation sources, optical fibres or larger radiation sources, integrating spheres are typically used. Products of this type can be selected here: Integrating sphere detectors
Irradiance sensitivity of broad band radiometers
A broadband radiometer for measuring irradiance contains one or more photodiodes. These are usually each equipped with an optical correction filter required for the intended actinic measurand and with a diffuser for cosine correction of the measurement geometry. Radiometers are widely used for routine measurements and where the use of spectroradiometers is not economical or where their advantages such as size, robustness and simplicity are important. Nevertheless, a high-quality radiometer is superior to many spectroradiometers available on the market in the specific application if used correctly, precisely characterised and corrected. Radiometers are used in radiation curing, measurement of photopic as well as scotopic illuminance in lux, photobiological actinic irradiance (erythema, ACGIH, etc.), integral irradiance for UV, VIS, and NIR or IR radiation, irradiance of excimer lamps, LEDs and other lamp types, as well as in the measurement of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR).
The Gigahertz Optik calibration laboratory is accredited for detectors with actinic weighting in the wavelength range from to .
Here, too, different detectors are offered for the dissemination of the measurand. We offer a wide range of different detectors that can be used for almost any application: Light Meters, Detectors, UV-VIS-NIR Radiometers
DC current of indicating instruments
An essential part of being able to carry out a precise measurement with a radiometer is the fully correct traceability of the measuring system, i.e. also the current gain and measurement of the transimpedance amplifier and data acquisition system. The special challenge here lies in the precise measurement of sometimes very small photocurrents in the pico-ampere (pA) range.
Gigahertz-Optik has a wide range of transimpedance amplifiers, transient recorders and display devices for optical radiation measurement quantities, according to the planned use (e.g. mobile, stationary, manual or remote), as well as the required number of signal channels and the planned measurement mode (CW, dose, pulse energy, temporal pulse progression).
Optometers, Amplifiers, Display Meters
ISO 17025 test laboratory
In a DAkkS-accredited test, a traceable measured value is generated or a measuring device is compared with a traceable measured value. The essential difference to calibration is that in a test, the measurand is not passed on, but the test object is placed in a relationship to a reference. But here, too, international recognition is guaranteed by the ILAC logo (International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation).

Narrow and broad band radiometers
This point extends the possible calibrations of 2b and 2c. With this, measurements of quantities other than spectral responsivity or measurement of integral irradiance are possible, such as relative spectral responsivity or the measurement of integral radiance responsivity. The limitation of the wavelength range during calibration is also extended here to a possible spectrum from to .
A narrow- or broad- band radiometer contains one or more photodiodes. These are each designed with an optical correction filter required for the intended measurand. Depending on the measurand, these detectors contain different input optics. Integrating spheres for radiant flux, cosine-matched diffusers for irradiance or various imaging optics for radiance. In an ISO 17025 test, typically the complete system consisting of detector and amplifier unit is considered to ensure appropriate traceability. We can carry out measurements on this type of detector within our ISO 17025 test laboratory for the wavelength range from to . Measurements of filter functions are also possible. This includes the measurement of both absolute and relative spectral response of different types of detectors with and without special input optics.
Appropriate narrow- and broad- band detectors can also be selected here: Light Meters, Detectors, UV-VIS-NIR Radiometers
Irradiance spectroradiometers
Spectroradiometers have become an indispensable part of optical metrology. Their versatile use in radiometry, in the measurement of LEDs, of artificial or natural solar radiation, of LASER, VCSEL and also in photometric or colorimetric measurement tasks has become the standard for the high precision required.
Spectral light meters and spectrometers are based on array detectors. Their special feature is the spectrally resolved measurements from which all photometric and radiometric measured quantities within the spectral measuring range of the device can be calculated. Depending on the input optics of the spectroradiometer and the intended use, we offer various tests for spectroradiometers in the wavelength range from to for the essential measured quantities irradiance, radiant flux and radiance.
We also offer all types of high-end spectroradiometers for the spectral ranges from to :
Spectral Light Meters, UV-VIS-NIR Spectroradiometers
Spectral irradiance
Spectral irradiance is, as already described in chapter 2a, the fundamental quantity in radiometry from which various measured quantities can be derived. In contrast to the DAkkS calibration, we are not limited to the two lamp types halogen and deuterium when testing radiators. Thus, we can also offer tests of e.g. LEDs, xenon emitters, HMI emitters or sun simulators. We are accredited for testing spectral irradiance in the wavelength range from to .
We also offer a corresponding LED standard which also fulfils the requirements of CIE 251:2023: LED based irradiance standard
Photometers
A photometer is a measuring device for the measurement of photometric quantities such as illuminance in lux (lx), luminance in candela per square metre or luminous flux in lumen (lm). A photometer consists of a detector that is adapted to the V( function of the human eye (luminous efficiency function) by means of a filter. Depending on the photometric quantity to be measured, a photometer has a corresponding input optics, such as integrating spheres, diffusers or imaging optics. Instruments of this type can be tested according to our accreditation.
Photometers for various measuring tasks are available from us: Light Meters for Photometry
Luminous flux and spectral radiant power
The essential measured variable in the characterisation of light sources is the spectral radiant power or spectral radiant flux, as well as the luminous flux (lm). The radiant flux is defined as the total power (W) emitted by a spotlight in all directions. The luminous flux is the photometrically weighted equivalent. These measured quantities are always important when different light sources, such as LEDs, halogen lamps, etc., have to be characterised according to total output or efficiency (luminous efficacy ).
Luminous flux and spectral flux are typically measured in an integrating sphere. Here, our laboratory is recommended due to years of know-how in the production and operation of integrating spheres.
We are accredited for luminous flux in lumen and spectral flux in watt (W) in the wavelength range from to .
Corresponding standard lamps with different beam characteristics (2-Pi and 4-Pi) are available from us: Spectral Radiant Flux / Luminous Flux Calibration Standards
Appropriate integrating spheres for operation and for further calibration processes are also available from us: Integrating Spheres
Luminance and spectral radiance
Area illuminators for pixel and intensity alignment of image sensors and cameras have luminance (cd/m2) or spectral radiance as essential measurement variables. These measurands play a decisive role in imaging, sensor technology and in display technology.
We are accredited for testing luminance and spectral radiance in the wavelength range from to .
We also offer homogeneous light sources as standard sources of spectral radiance or luminance. These can also be individually equipped with different LEDs or halogen spotlights with filters:
Spectral Radiance / Luminance Calibration Standards
DAkkS – Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle
The DAkkS is the national accreditation body of the Federal Republic of Germany. According to Regulation (EG) No. 765/2008 and the Accreditation Body Act (AkkStelleG), it acts in the public interest as the sole service provider for accreditation in Germany.
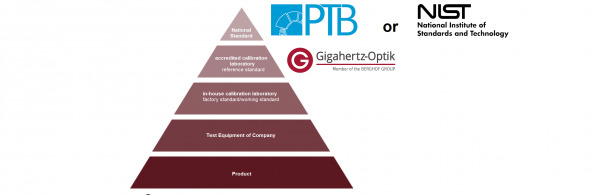
The basic idea of the DAkkS is to delegate as many PTB responsibilities as possible, i.e. responsibilities of the National Metrology Institute (NMI) as well as NIST, METAS, NPL (see Chapter 5) to industry. This includes the calibration of measuring and testing equipment, for example. The DAkkS ensures that the traceability of measuring and testing equipment to the national institutes is guaranteed by regular control (Gigahertz-Optik is accredited by the DAkkS as a calibration laboratory under the number D-K-15047-01-00 and as a testing laboratory under the number D-PL-15047-01-00).
This allows calibration laboratories accredited by the DAkkS to offer calibrations which are traceable to national calibration standards. An uninterrupted traceable calibration chain to national standards is of particular importance for manufacturers of measuring and testing equipment in order to be competitive in national and international markets. Furthermore, this is necessary for any quality management system.
The qualification of traceability to national standards is the task of the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB), which is the German National Metrology Institute. The PTB defines, realises, maintains and disseminates the physical quantities of the SI system, e.g. metre, second, candela, etc.
To ensure this, comparable standards must be used. A calibration based on SI units, which in turn are comparable and measurable, can be audited and thus checked. With the DIN ISO 9000 standard, the relationship between quality management and calibration is partly intertwined to ensure continuous control of measuring and testing equipment.
Without exception, DAkkS accredited testing and calibration laboratories must meet the requirements of DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025 (General requirements for a calibration laboratory). DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025 replaced EN 45001 and ISO/IEC Guide 25 in 1999.
The European role of DAkkS lies in its membership of the European Cooperation for Accredited Laboratories (EAL) in Rotterdam. This was founded by the "Western European Calibration Cooperation" (WECC) and the "Western European Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation" (WELAC) in 1994. Within the EAL, various institutes cooperate with the aim of ensuring that EAL calibration laboratories receive international recognition.
Further information: http://www.dakks.de
NMI – National Metrology Institute
PTB – Physikalisch Technische Bundesanstalt
The Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) is the national metrology institute of Germany, and thus the highest technical authority regarding metrology in Germany. PTB defines, realises, maintains and disseminates the physical quantities of the SI system, such as the metre, second, candela, etc.
PTB is the official accreditation institution for DAkkS calibration laboratories such as Gigahertz-Optik in optical measurement quantities. In addition, PTB is committed to the bilateral acceptance of international standards. Through its activities in 1995, a Memorandum of Understanding was signed between the "National Institute of Standards and Technology" (NIST-USA) and the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) concerning the international traceability of standards. The equivalence of the national standards of NIST and those of PTB for the SI units luminous intensity and luminous flux was officially published in April 1999.
Further information about the PTB can be found here: http://www.ptb.de
NIST – National Institute of Standards and Technology
NIST is the National Metrology Institute of the USA. As part of NIST's mission, the Optical Technologies Division develops, improves and maintains national standards for spectroradiometry, photometry, colorimetry and spectral photometry. In addition to national standards, services are also offered in the spectral range from UV to IR. The calibrations of NIST should meet the highest requirements for accuracy. In addition, NIST publishes technical articles and recommendations concerning optical metrology.
Further information about NIST and its activities can be found here: https://www.nist.gov/
NPL - National Physical Laboratory
The NPL is the UK's national metrology institute. NPL's Optical Measurement Group provides services that form the backbone of industrial and academic optical metrology in the UK. Primary standards and units are maintained, and scientific research is carried out to improve quality. The NPL pursues industrial and academic objectives in the spectral range UV to IR.
Measurement and calibration services include characterisation and calibration of all types of optical radiation sources, optical radiation detectors and accessories, optical properties of materials and components such as colour, gloss, opacity, etc.
More information at https://www.npl.co.uk/
METAS – Eidgenössisches Institut für Metrologie
METAS is the national metrology institute of Switzerland. The specialist area of radiometry and photometry covers a wide range of calibrations and measurement services in photometry, radiometry and photonics. Special attention is also given to the performance of photometric tests and the measurement of vehicle lighting.
METAS conducts extensive research in the field of optical reflection and other optical properties.
Further information at: https://www.metas.ch/